What is the meaning of gross income and why is it important to understand? In this article, we will explore whether gross income is calculated before or after taxes and how to determine it.
Definition of gross income
Gross income refers to the total amount of money a person earns, typically in the form of a paycheck, before taxes are withheld. It plays a role in determining an individual’s eligibility for home mortgages and is used in the calculation of state and federal income taxes.
For instance, let’s assume your gross weekly income is $400. However, what is your net income? You actually receive $325 after taxes and other deductions are taken out. Similarly, you can determine your own gross income.
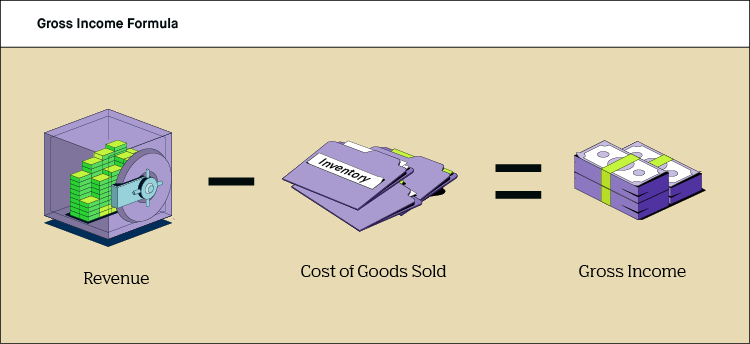
How does gross income work?
Another straightforward definition of gross income is the complete sum of your salary. Bonuses are also included in gross income. For hourly workers, the gross income shown on a pay stub is calculated by multiplying the hourly wage by the number of hours worked. W-2 forms, which employees receive from their employers during tax filing, also display the gross income amount.
Aside from income from a W-2 job, total gross income can come from various sources. For example, you might earn money through alimony, consulting, self-employment, freelancing, or other means.
Certain types of income are not subject to taxes, so there is no need to report them on your tax returns. This includes income from state bonds, municipal sources, as well as gifts, inheritances, social security benefits, and specific life insurance payouts.
Note! Form W-2 is an annual document called the “Wage and Tax Statement” that reports your taxable income earned from an employer to both you and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Comparing gross and net incomes
Gross income or pay represents your total income before taxes, while net income refers to the amount you take home after taxes have been deducted.
After deductions like taxes are removed, the net income is significantly lower than the gross income. Employers are required to deduct federal taxes, social security taxes, and other applicable deductions. Additionally, they may deduct any chosen benefits such as healthcare premiums or contributions to flexible spending or health savings accounts.
Therefore, the next time someone asks about your gross monthly income or salary, you can simply provide the actual pay you receive without any deductions.

Definition of adjusted gross income (pay)
By combining all sources of earnings, you can determine your overall income and understand how expenses and deductions can reduce your gross income. This, in turn, lowers your tax liability.
The following factors can decrease your gross income:
- Expenses related to being an educator.
- Business-related costs like supplies, transportation, or equipment rental expenses.
- Deductions for self-employed individuals participating in SIMPLE IRA, SEP-IRA, and 401(k) plans.
- Deductible employment taxes.
- Contributions made to certain retirement funds.
- Penalties from financial institutions for early withdrawals of savings.
- Interest paid on student loans (with specific qualifications).
- Deductions for health savings accounts (HSAs).
- Alimony payments.
Adjusted gross income, which serves as the basis for your taxation, is the income you have left after these deductions are subtracted from your earnings.
The bottom line
Understanding the meaning of gross income is crucial as you may need to calculate it at some point. However, defining gross income is no longer a challenge. You can determine your monthly gross income by reviewing the payslip provided by your employer and adding any additional earnings from side jobs like freelancing or rental property income.